#Data Warehouse Application
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Data Warehouse Services
#QuellSoft#Data Warehouse Services#Data Warehousing#Cloud Applications Services#Data Warehousing Essentials#Data Warehouse Application#custom website development#website design and development#website optimization#app development software
0 notes
Text
5G-Powered Drones: Ericsson, Qualcomm And Dronus Collaboration In Developing Autonomous Drone Solutions

5G mmWave technology for industrial use. Ericsson, Qualcomm, and Dronus Collaboration in developing autonomous drone solutions. The world of industrial automation is on the cusp of a revolution, and at the forefront is a powerful combination, of 5G technology and autonomous drones. A recent collaboration between Ericsson, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., and Dronus provides a glimpse into this exciting future.
#5G drones#Industrial automation#Indoor drone applications#Warehouse inventory management#mmWave 5G technology#Autonomous drones#Industry 4.0#5G smart factory#(PoC)#Qualcomm QRB5165 processor#Telit Cinterion#mmWave#Industrial M.2 data card#5G Modem-RF System#Native mmWave connectivity#High-performance 5G connection#Bandwidth-intensive industrial operations#drone
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
UltiHash’s Sustainable Data Infrastructure Tackles AI Storage Challenges
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/ultihashs-sustainable-data-infrastructure-tackles-ai-storage-challenges/
UltiHash’s Sustainable Data Infrastructure Tackles AI Storage Challenges
UltiHash, a provider of high-performance and eco-friendly data storage solutions, has launched its object storage platform to address critical issues in AI data storage. This development aims to resolve mounting challenges in the AI industry related to infrastructure costs and environmental sustainability. The new platform enhances performance for data-heavy applications, including generative AI and advanced analytics, offering scalable and sustainable solutions for data management.
As the AI industry grows, projected to reach $407 billion by 2027 according to Forbes, the demand for data storage has surged. AI model training, which relies on massive datasets, often strains current storage infrastructure due to inefficiency, leading to high costs and a significant environmental footprint. UltiHash’s new platform is designed to solve these issues, providing high-performance storage while reducing both operational expenses and environmental impact.
Key Features of UltiHash’s Platform
UltiHash’s platform introduces several key innovations, including:
Advanced Deduplication: Reducing data volumes by up to 60% by eliminating redundant data at the byte level, minimizing storage needs and bandwidth usage.
Scalability: Built for organizations with rapidly growing data needs, the platform scales easily to petabytes and beyond, supporting continuous data expansion.
Enhanced Performance: With 250% faster read speeds compared to AWS S3, the platform improves data throughput for both read and write operations, essential for high-performance applications.
Interoperability: Fully compatible with S3 APIs and designed for seamless integration with both cloud and on-premises infrastructures, including Kubernetes-native environments.
Data Resiliency: Built-in erasure coding ensures data is protected even during hardware failures, safeguarding against system disruptions.
These features position UltiHash as a critical player in the AI data storage landscape, especially for organizations adopting data lakehouse architectures. By combining the scalability of data lakes with the query efficiency of data warehouses, the platform supports diverse data formats while optimizing performance and resource usage.
Building on Recent Success: $2.5M Pre-Seed Funding
UltiHash’s latest announcement follows its successful $2.5 million pre-seed funding round in December 2023, led by Inventure, alongside investors like PreSeedVentures, Tiny VC, and Sequoia Capital-affiliated angel investors. The funding supports UltiHash’s efforts to enhance its platform and accelerate market entry.
The company’s entry into the market comes as data growth reaches unprecedented levels. IDC projects that global digital data will hit 175 zettabytes by 2025, each zettabyte contributing the carbon footprint of approximately two million people annually. This rapid increase in data generation presents both operational and environmental challenges, with existing storage solutions often requiring significant cost outlays and energy consumption. UltiHash’s platform aims to break this cycle by reducing the overall storage demand while maintaining high performance.
A Future of Sustainable, High-Performance Storage
By reducing the data stored through advanced deduplication, UltiHash enables companies to scale their data operations sustainably. This technology addresses the core issue of balancing scalability with affordability, which has traditionally constrained data-driven industries, including AI, telecom, manufacturing, and automotive.
“The AI revolution is generating data at an unprecedented rate, and traditional storage solutions are struggling to keep pace,” says Tom Lüdersdorf, Co-Founder and CEO of UltiHash. “The future of storage will make it possible to avoid ballooning data costs without compromising on speed.”
As data continues to fuel innovation in AI and other industries, UltiHash‘s platform is poised to play a crucial role in enabling sustainable data growth. Its focus on reducing both the environmental toll and the financial burden of large-scale data storage could reshape how organizations approach data infrastructure.
#2023#250#ai#ai model#Analytics#APIs#applications#approach#Artificial Intelligence#automotive#AWS#billion#Building#Byte#carbon#carbon footprint#CEO#Cloud#coding#Companies#continuous#Critical Issues#data#data lakehouse#data lakes#Data Management#data storage#data storage solutions#data warehouses#data-driven
0 notes
Text
The reason you can’t buy a car is the same reason that your health insurer let hackers dox you

On July 14, I'm giving the closing keynote for the fifteenth HACKERS ON PLANET EARTH, in QUEENS, NY. Happy Bastille Day! On July 20, I'm appearing in CHICAGO at Exile in Bookville.

In 2017, Equifax suffered the worst data-breach in world history, leaking the deep, nonconsensual dossiers it had compiled on 148m Americans and 15m Britons, (and 19k Canadians) into the world, to form an immortal, undeletable reservoir of kompromat and premade identity-theft kits:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2017_Equifax_data_breach
Equifax knew the breach was coming. It wasn't just that their top execs liquidated their stock in Equifax before the announcement of the breach – it was also that they ignored years of increasingly urgent warnings from IT staff about the problems with their server security.
Things didn't improve after the breach. Indeed, the 2017 Equifax breach was the starting gun for a string of more breaches, because Equifax's servers didn't just have one fubared system – it was composed of pure, refined fubar. After one group of hackers breached the main Equifax system, other groups breached other Equifax systems, over and over, and over:
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/equifax-password-username-admin-lawsuit-201118316.html
Doesn't this remind you of Boeing? It reminds me of Boeing. The spectacular 737 Max failures in 2018 weren't the end of the scandal. They weren't even the scandal's start – they were the tipping point, the moment in which a long history of lethally defective planes "breached" from the world of aviation wonks and into the wider public consciousness:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_accidents_and_incidents_involving_the_Boeing_737
Just like with Equifax, the 737 Max disasters tipped Boeing into a string of increasingly grim catastrophes. Each fresh disaster landed with the grim inevitability of your general contractor texting you that he's just opened up your ceiling and discovered that all your joists had rotted out – and that he won't be able to deal with that until he deals with the termites he found last week, and that they'll have to wait until he gets to the cracks in the foundation slab from the week before, and that those will have to wait until he gets to the asbestos he just discovered in the walls.
Drip, drip, drip, as you realize that the most expensive thing you own – which is also the thing you had hoped to shelter for the rest of your life – isn't even a teardown, it's just a pure liability. Even if you razed the structure, you couldn't start over, because the soil is full of PCBs. It's not a toxic asset, because it's not an asset. It's just toxic.
Equifax isn't just a company: it's infrastructure. It started out as an engine for racial, political and sexual discrimination, paying snoops to collect gossip from nosy neighbors, which was assembled into vast warehouses full of binders that told bank officers which loan applicants should be denied for being queer, or leftists, or, you know, Black:
https://jacobin.com/2017/09/equifax-retail-credit-company-discrimination-loans
This witch-hunts-as-a-service morphed into an official part of the economy, the backbone of the credit industry, with a license to secretly destroy your life with haphazardly assembled "facts" about your life that you had the most minimal, grudging right to appeal (or even see). Turns out there are a lot of customers for this kind of service, and the capital markets showered Equifax with the cash needed to buy almost all of its rivals, in mergers that were waved through by a generation of Reaganomics-sedated antitrust regulators.
There's a direct line from that acquisition spree to the Equifax breach(es). First of all, companies like Equifax were early adopters of technology. They're a database company, so they were the crash-test dummies for ever generation of database. These bug-riddled, heavily patched systems were overlaid with subsequent layers of new tech, with new defects to be patched and then overlaid with the next generation.
These systems are intrinsically fragile, because things fall apart at the seams, and these systems are all seams. They are tech-debt personified. Now, every kind of enterprise will eventually reach this state if it keeps going long enough, but the early digitizers are the bow-wave of that coming infopocalypse, both because they got there first and because the bottom tiers of their systems are composed of layers of punchcards and COBOL, crumbling under the geological stresses of seventy years of subsequent technology.
The single best account of this phenomenon is the British Library's postmortem of their ransomware attack, which is also in the running for "best hard-eyed assessment of how fucked things are":
https://www.bl.uk/home/british-library-cyber-incident-review-8-march-2024.pdf
There's a reason libraries, cities, insurance companies, and other giant institutions keep getting breached: they started accumulating tech debt before anyone else, so they've got more asbestos in the walls, more sagging joists, more foundation cracks and more termites.
That was the starting point for Equifax – a company with a massive tech debt that it would struggle to pay down under the most ideal circumstances.
Then, Equifax deliberately made this situation infinitely worse through a series of mergers in which it bought dozens of other companies that all had their own version of this problem, and duct-taped their failing, fucked up IT systems to its own. The more seams an IT system has, the more brittle and insecure it is. Equifax deliberately added so many seams that you need to be able to visualized additional spatial dimensions to grasp them – they had fractal seams.
But wait, there's more! The reason to merge with your competitors is to create a monopoly position, and the value of a monopoly position is that it makes a company too big to fail, which makes it too big to jail, which makes it too big to care. Each Equifax acquisition took a piece off the game board, making it that much harder to replace Equifax if it fucked up. That, in turn, made it harder to punish Equifax if it fucked up. And that meant that Equifax didn't have to care if it fucked up.
Which is why the increasingly desperate pleas for more resources to shore up Equifax's crumbling IT and security infrastructure went unheeded. Top management could see that they were steaming directly into an iceberg, but they also knew that they had a guaranteed spot on the lifeboats, and that someone else would be responsible for fishing the dead passengers out of the sea. Why turn the wheel?
That's what happened to Boeing, too: the company acquired new layers of technical complexity by merging with rivals (principally McDonnell-Douglas), and then starved the departments that would have to deal with that complexity because it was being managed by execs whose driving passion was to run a company that was too big to care. Those execs then added more complexity by chasing lower costs by firing unionized, competent, senior staff and replacing them with untrained scabs in jurisdictions chosen for their lax labor and environmental enforcement regimes.
(The biggest difference was that Boeing once had a useful, high-quality product, whereas Equifax started off as an irredeemably terrible, if efficient, discrimination machine, and grew to become an equally terrible, but also ferociously incompetent, enterprise.)
This is the American story of the past four decades: accumulate tech debt, merge to monopoly, exponentially compound your tech debt by combining barely functional IT systems. Every corporate behemoth is locked in a race between the eventual discovery of its irreparable structural defects and its ability to become so enmeshed in our lives that we have to assume the costs of fixing those defects. It's a contest between "too rotten to stand" and "too big to care."
Remember last February, when we all discovered that there was a company called Change Healthcare, and that they were key to processing virtually every prescription filled in America? Remember how we discovered this? Change was hacked, went down, ransomed, and no one could fill a scrip in America for more than a week, until they paid the hackers $22m in Bitcoin?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2024_Change_Healthcare_ransomware_attack
How did we end up with Change Healthcare as the linchpin of the entire American prescription system? Well, first Unitedhealthcare became the largest health insurer in America by buying all its competitors in a series of mergers that comatose antitrust regulators failed to block. Then it combined all those other companies' IT systems into a cosmic-scale dog's breakfast that barely ran. Then it bought Change and used its monopoly power to ensure that every Rx ran through Change's servers, which were part of that asbestos-filled, termite-infested, crack-foundationed, sag-joisted teardown. Then, it got hacked.
United's execs are the kind of execs on a relentless quest to be too big to care, and so they don't care. Which is why their they had to subsequently announce that they had suffered a breach that turned the complete medical histories of one third of Americans into immortal Darknet kompromat that is – even now – being combined with breach data from Equifax and force-fed to the slaves in Cambodia and Laos's pig-butchering factories:
https://www.cnn.com/2024/05/01/politics/data-stolen-healthcare-hack/index.html
Those slaves are beaten, tortured, and punitively raped in compounds to force them to drain the life's savings of everyone in Canada, Australia, Singapore, the UK and Europe. Remember that they are downstream of the forseeable, inevitable IT failures of companies that set out to be too big to care that this was going to happen.
Failures like Ticketmaster's, which flushed 500 million users' personal information into the identity-theft mills just last month. Ticketmaster, you'll recall, grew to its current scale through (you guessed it), a series of mergers en route to "too big to care" status, that resulted in its IT systems being combined with those of Ticketron, Live Nation, and dozens of others:
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/05/31/business/ticketmaster-hack-data-breach.html
But enough about that. Let's go car-shopping!
Good luck with that. There's a company you've never heard. It's called CDK Global. They provide "dealer management software." They are a monopolist. They got that way after being bought by a private equity fund called Brookfield. You can't complete a car purchase without their systems, and their systems have been hacked. No one can buy a car:
https://www.cnn.com/2024/06/27/business/cdk-global-cyber-attack-update/index.html
Writing for his BIG newsletter, Matt Stoller tells the all-too-familiar story of how CDK Global filled the walls of the nation's auto-dealers with the IT equivalent of termites and asbestos, and lays the blame where it belongs: with a legal and economics establishment that wanted it this way:
https://www.thebignewsletter.com/p/a-supreme-court-justice-is-why-you
The CDK story follows the Equifax/Boeing/Change Healthcare/Ticketmaster pattern, but with an important difference. As CDK was amassing its monopoly power, one of its execs, Dan McCray, told a competitor, Authenticom founder Steve Cottrell that if he didn't sell to CDK that he would "fucking destroy" Authenticom by illegally colluding with the number two dealer management company Reynolds.
Rather than selling out, Cottrell blew the whistle, using Cottrell's own words to convince a district court that CDK had violated antitrust law. The court agreed, and ordered CDK and Reynolds – who controlled 90% of the market – to continue to allow Authenticom to participate in the DMS market.
Dealers cheered this on: CDK/Reynolds had been steadily hiking prices, while ingesting dealer data and using it to gouge the dealers on additional services, while denying dealers access to their own data. The services that Authenticom provided for $35/month cost $735/month from CDK/Reynolds (they justified this price hike by saying they needed the additional funds to cover the costs of increased information security!).
CDK/Reynolds appealed the judgment to the 7th Circuit, where a panel of economists weighed in. As Stoller writes, this panel included monopoly's most notorious (and well-compensated) cheerleader, Frank Easterbrook, and the "legendary" Democrat Diane Wood. They argued for CDK/Reynolds, demanding that the court release them from their obligations to share the market with Authenticom:
https://caselaw.findlaw.com/court/us-7th-circuit/1879150.html
The 7th Circuit bought the argument, overturning the lower court and paving the way for the CDK/Reynolds monopoly, which is how we ended up with one company's objectively shitty IT systems interwoven into the sale of every car, which meant that when Russian hackers looked at that crosseyed, it split wide open, allowing them to halt auto sales nationwide. What happens next is a near-certainty: CDK will pay a multimillion dollar ransom, and the hackers will reward them by breaching the personal details of everyone who's ever bought a car, and the slaves in Cambodian pig-butchering compounds will get a fresh supply of kompromat.
But on the plus side, the need to pay these huge ransoms is key to ensuring liquidity in the cryptocurrency markets, because ransoms are now the only nondiscretionary liability that can only be settled in crypto:
https://locusmag.com/2022/09/cory-doctorow-moneylike/
When the 7th Circuit set up every American car owner to be pig-butchered, they cited one of the most important cases in antitrust history: the 2004 unanimous Supreme Court decision in Verizon v Trinko:
https://www.oyez.org/cases/2003/02-682
Trinko was a case about whether antitrust law could force Verizon, a telcoms monopolist, to share its lines with competitors, something it had been ordered to do and then cheated on. The decision was written by Antonin Scalia, and without it, Big Tech would never have been able to form. Scalia and Trinko gave us the modern, too-big-to-care versions of Google, Meta, Apple, Microsoft and the other tech baronies.
In his Trinko opinion, Scalia said that "possessing monopoly power" and "charging monopoly prices" was "not unlawful" – rather, it was "an important element of the free-market system." Scalia – writing on behalf of a unanimous court! – said that fighting monopolists "may lessen the incentive for the monopolist…to invest in those economically beneficial facilities."
In other words, in order to prevent monopolists from being too big to care, we have to let them have monopolies. No wonder Trinko is the Zelig of shitty antitrust rulings, from the decision to dismiss the antitrust case against Facebook and Apple's defense in its own ongoing case:
https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/documents/cases/073_2021.06.28_mtd_order_memo.pdf
Trinko is the origin node of too big to care. It's the reason that our whole economy is now composed of "infrastructure" that is made of splitting seams, asbestos, termites and dry rot. It's the reason that the entire automotive sector became dependent on companies like Reynolds, whose billionaire owner intentionally and illegally destroyed evidence of his company's crimes, before going on to commit the largest tax fraud in American history:
https://www.wsj.com/articles/billionaire-robert-brockman-accused-of-biggest-tax-fraud-in-u-s-history-dies-at-81-11660226505
Trinko begs companies to become too big to care. It ensures that they will exponentially increase their IT debt while becoming structurally important to whole swathes of the US economy. It guarantees that they will underinvest in IT security. It is the soil in which pig butchering grew.
It's why you can't buy a car.
Now, I am fond of quoting Stein's Law at moments like this: "anything that can't go on forever will eventually stop." As Stoller writes, after two decades of unchallenged rule, Trinko is looking awfully shaky. It was substantially narrowed in 2023 by the 10th Circuit, which had been briefed by Biden's antitrust division:
https://law.justia.com/cases/federal/appellate-courts/ca10/22-1164/22-1164-2023-08-21.html
And the cases of 2024 have something going for them that Trinko lacked in 2004: evidence of what a fucking disaster Trinko is. The wrongness of Trinko is so increasingly undeniable that there's a chance it will be overturned.
But it won't go down easy. As Stoller writes, Trinko didn't emerge from a vacuum: the economic theories that underpinned it come from some of the heroes of orthodox economics, like Joseph Schumpeter, who is positively worshipped. Schumpeter was antitrust's OG hater, who wrote extensively that antitrust law didn't need to exist because any harmful monopoly would be overturned by an inevitable market process dictated by iron laws of economics.
Schumpeter wrote that monopolies could only be sustained by "alertness and energy" – that there would never be a monopoly so secure that its owner became too big to care. But he went further, insisting that the promise of attaining a monopoly was key to investment in great new things, because monopolists had the economic power that let them plan and execute great feats of innovation.
The idea that monopolies are benevolent dictators has pervaded our economic tale for decades. Even today, critics who deplore Facebook and Google do so on the basis that they do not wield their power wisely (say, to stamp out harassment or disinformation). When confronted with the possibility of breaking up these companies or replacing them with smaller platforms, those critics recoil, insisting that without Big Tech's scale, no one will ever have the power to accomplish their goals:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/18/urban-wildlife-interface/#combustible-walled-gardens
But they misunderstand the relationship between corporate power and corporate conduct. The reason corporations accumulate power is so that they can be insulated from the consequences of the harms they wreak upon the rest of us. They don't inflict those harms out of sadism: rather, they do so in order to externalize the costs of running a good system, reaping the profits of scale while we pay its costs.
The only reason to accumulate corporate power is to grow too big to care. Any corporation that amasses enough power that it need not care about us will not care about it. You can't fix Facebook by replacing Zuck with a good unelected social media czar with total power over billions of peoples' lives. We need to abolish Zuck, not fix Zuck.
Zuck is not exceptional: there were a million sociopaths whom investors would have funded to monopolistic dominance if he had balked. A monopoly like Facebook has a Zuck-shaped hole at the top of its org chart, and only someone Zuck-shaped will ever fit through that hole.
Our whole economy is now composed of companies with sociopath-shaped holes at the tops of their org chart. The reason these companies can only be run by sociopaths is the same reason that they have become infrastructure that is crumbling due to sociopathic neglect. The reckless disregard for the risk of combining companies is the source of the market power these companies accumulated, and the market power let them neglect their systems to the point of collapse.
This is the system that Schumpeter, and Easterbrook, and Wood, and Scalia – and the entire Supreme Court of 2004 – set out to make. The fact that you can't buy a car is a feature, not a bug. The pig-butcherers, wallowing in an ocean of breach data, are a feature, not a bug. The point of the system was what it did: create unimaginable wealth for a tiny cohort of the worst people on Earth without regard to the collapse this would provoke, or the plight of those of us trapped and suffocating in the rubble.

Support me this summer on the Clarion Write-A-Thon and help raise money for the Clarion Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers' Workshop!

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/06/28/dealer-management-software/#antonin-scalia-stole-your-car

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#matt stoller#monopoly#automotive#trinko#antitrust#trustbusting#cdk global#brookfield#private equity#dms#dealer management software#blacksuit#infosec#Authenticom#Dan McCray#Steve Cottrell#Reynolds#frank easterbrook#schumpeter
996 notes
·
View notes
Text
I swear to god it feels like spinning in hamster wheel. I'll apply for a job, get the email that I didn't get the job, and then a week later see the same job posted by the same company. LinkedIn tracks what jobs you've already applied for so I know it's not the same one. It's a new posting for the same job.
I put in 20-30 applications a day and the ADHD makes things like company names not stick in my mind - that and the fact that I don't give a single fuck about these companies. So it takes seeing these names a few times before they stick with me. Lensa. Robert Half. Brooksource. Data entry specialist bookkeeper administrative assistant tech support desk customer service representative technician consultant advisor
I feel like none of these jobs are even real and LinkedIn is just as Dead Internet Theory as every other social media and I'm just pinning my resume on a dusty corkboard in an abandoned warehouse and then sitting home confused that no one is calling me
#my words#frustration#I literally have 12 years customer service experience#8 years help desk experience#4 years work-from-home experience#two certifications#and a fucking bachelors degree in IT#why can't I get a $15/hour level 1 help desk job????????
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bonus
Happy particular Monday! Here’s a story for it, which came about mostly because I wanted to put a couple of people into a clichéd situation, and then I had to do leadup and aftermath... anyway, it’s intended to be a two-parter (yes, I know; aspirations) set in a not-entirely-canonical season 4, in which the Warehouse did get brought back and Helena did leave without explanation, BUT Artie doesn’t go full Father Data and Leena doesn’t suffer the consequences—mostly because Mrs. Frederic has sensed some badness to come and thus sent Artie and Leena away. Because why not? Also I have Claudia jumping into Caretakering, and even a bit of Artieing, with some enthusiasm.
P.S. I know I haven’t yet finished last year’s Christmas story—that’s a pain point—but I genuinely am working to get back on various horses, including that one. Weather (in all senses) permitting.
Bonus
“I genuinely cannot believe we’re stuck in an elevator,” Myka says. It may be the most true statement to which she’s ever given voice.
****
SEVERAL HOURS EARLIER...
Myka’s reasonably pleasant thought, burring along as background to her monotonous tasks, is I don’t mind this. She and Steve are in the Warehouse office early in the morning, doing file inventory, and it’s true: she doesn’t mind it. It’s a little lacking as a holiday activity, but with Artie, Leena, and Pete all away, “lacking” is pretty much the flavor of the moment.
Claudia pokes her head in and says, “Ping.” She’s unenthusiastic, speaking of lacking. Where’s the usual revving about what it might be this time? “At some midwestern accounting firm, because it’s important to have a boring Christmas.”
Ah. “An accounting artifact?” Myka asks. Speaking further of lacking: here, it’s artifacty zing. Then again, artifacty zing got Myka trapped in Alice’s mirror, among other catastrophes, so maybe boring isn’t so bad. “Balance sheets?” she ventures. “Pluses and minuses?”
“Some people at this pingy company just got extremely large Christmas bonuses,” Claudia says, “and some got their pay extremely docked. So yeah, ‘balance sheets, pluses and minuses’ just about covers it. Probably. I mean, I might be trying to manage expectations here.”
Claudia’s certainly right, in that getting one’s hopes up—about anything (or anyone)—is a fool’s game.
But still, there’s something to be said for boring-but-remunerative, even if only for some people... what a nice idea. “I’d like a Christmas bonus someday,” Myka says, “instead of a Christmas penalty. Which I think pretty accurately describes the Pete-plus-artifacts situation.”
“It’s two days before Christmas, and he hasn’t done anything yet,” Claudia says. “That you know of,” she amends.
“Because he’s been with his family in Ohio for the past week,” Myka points out, and she’s gratified when Claudia rolls her eyes. It’s practically a concession.
Steve says, “It’s inappropriate to say ‘Christmas’ bonus these days. It’s ‘end-of-year.’” The contribution suggests he’s listening with only one ear.
“I wish appropriateness mattered here,” Myka says, not really to him but in general. Who knows how a Warehouse HR department would make heads or tails of the application of employment laws—much less employment niceties? “Not that it makes a difference. Christmas, end-of-year... call it Fred, and we still wouldn’t get one.”
“If I ever do get a bonus, I’m absolutely naming it Fred,” Claudia declares.
Myka shakes her head. “Poor Fred. Doomed to be injected right back into the discretionary economy.”
“Inject-o-what are you even talking about?”
“Just a guess, but: you’d spend it on things you don’t need.”
Claudia harrumphs. “Thanks for lumping me in with the avocado-toast-and-Starbucks crowd. My fiscaling is way more responsible.”
“Really? What would you use Fred for?”
“Asus VG278HE gaming monitor. Plus a graphics card, maybe the Nvidia GTX 690, depending on how hefty Fred is.” At Myka’s snort, Claudia challenges, “Fine, where would you inject it?”
“My Roth IRA,” Myka says immediately. She’s not sure what assets her evil, crazy, or dead self will need in retirement, but given the many and varied forms each of those, or combinations thereof, could take, it seems like a good idea to have a financial plan in place. That’s another thing a Warehouse HR department might be useful for...
“You’re the actual human manifestation of an accounting artifact,” Claudia accuses. “Speaking of which, here’s the deal. I gotta stay here—some Mrs.-F homeworky stuff—and Steve’s busy reassuring all the misfit toys in the building that Leena hasn’t deserted them forever. And I’d say ignore the ping entirely, but your never know what’ll go viral, and I bet Artie’d say the last thing we need is another financial crisis. Or maybe you’d say it. Anyway, you’re it. And for your backup, when you get to Cleveland—”
Myka groans. “Cleveland? Seriously? Pete’s going to be so mad about you pulling him away from the family.”
“I’m not pulling him away,” Claudia says, blinking like she’s some innocent little lamb.
Myka groans again. “You’re making me do it?”
Claudia shrugs. “Sure. Why not. You’re partners, right? But here’s some advice: wait till you get there to call him. You know, put off the misery, if that’s what it is, as long as possible. Besides—more advice—I really think you should spend your travel time thinking about bonuses. Who gets ’em and why. Because what’s a bonus, really?”
“An economic stimulus whose nametag reads ‘Fred,’ if I’m understanding things correctly.”
“We’ll see what you think about that when you get to Cleveland.”
“On the day before Christmas eve,” Myka grouses. “By the way, that’s a whole lot of ‘advice,’ coming from somebody who’s over a decade younger than I am and not technically my boss.”
“By the way,” Claudia mimics, archly mocking, “we’ll see what you think about that too.”
“When I get to Cleveland?”
“When you get to Cleveland. On the day before Christmas eve.”
“Sounds like the title of a lesser Christmas carol,” Steve says—he’s tuned back in to the conversation. He then says, with his grin that curves so impish, “Think we could get Mariah Carey to sing it? It’s a hit if we get her, right, no matter how lesser?”
“‘When You Get to Cleveland on the Day Before Christmas Eve?’” Claudia skeptics. “Hit-wise, that’s gonna need a lot more power: Mariah dueting with Darlene Love at the very least. Plus we’ll need a Destiny’s Child reunion for at least one chorus.”
“Thanks for reinforcing my sense of how awful this is likely to be,” Myka tells them both, and Steve’s grin turns apologetic.
Claudia, however, shrugs. “Maybe you’ll sing it different.”
Myka is now the one to roll her eyes. “I won’t sing it at all.”
Surprisingly, Claudia doesn’t go with another eyeroll. “We’ll see,” she says, and Myka is struck by the Mrs.-Frederic resonance in her words. Does the homework include practicing the enigmatic tone?
Steve looks up and catches Myka’s eye. He winks. Myka would wink back, but he would probably interpret that as her saying she understands what’s happening. And that would be a lie: serious enough, probably, to make him wince and massage his temples.
So Myka just blinks—not Morse or any other code, just basic eye-moistening blinks. Then she goes upstairs to collect her always-packed travel bag for her trip to Cleveland.
****
Her flight departs late, of course; it’s December in South Dakota. But that’s this-time fine, because it allows Myka a necessary excess of opportunity to prep her Pete-placation. Under her breath, she practices the delivery of such words as “shorthanded��� and “necessary,” aiming for maximum sincerity.
When she at last emerges from her Cleveland Hopkins jetway, that extensive prep deserts her entirely, for what awaits her is the manifestation of a Christmas wish she has worked overtime to convince herself would not, could not possibly be granted:
Helena.
Whose arms are crossed, and whose posture betrays that her foot might recently have been tapping out impatience with the plane’s tardy arrival. The attitude is so normal, so entirely of-the-world (rather than of-its-imminent-end), that Myka wants to reverse course, get back on the plane and redisembark, just so she might meet it again, meet it and refeel this wash of absolute relief at seeing Helena impatient in an airport.
Devious, Claudia, Myka thinks. Outstandingly devious. “Hello, Fred,” she murmurs, then tries, in the ten seconds she has before she and Helena are in proximity to speak, to engage in a far more consequential prep.
For Helena has been gone—has been, as Myka put it to Steve not so long ago, “god knows where”—since shortly after the Warehouse did not explode. She was there, in the Warehouse, but then she was gone, and Myka was told only that Helena had “matters to attend to.” God presumably also knew what those matters were, but Myka hadn’t, in the wake of that first moment of absence, and hasn’t since, been able to pry any information about matters or their whereabouts out of anyone, divine or otherwise.
And through the seemingly endless wondering, Myka’s mind and heart have gnawed themselves ragged.
Until this moment, when the wondering and gnawing end: now her blood speeds, coursing with urgency even as everything else seems to slow.... her movements, her reactions, her thinking, all are sluggish, unresponsive; only her blood matters. This blood knowledge. For all her wondering, she’s been avoiding gnawing her way to that answer.
“Claudia said you needed backup” are Helena’s words when they meet.
Myka’s attempt at prep has fallen grievously short—not that she could have risen to such an occasion, not when hearing that voice for the first time in some time, and certainly not when faced with what her blood’s embarrassing insistence has forced her to confront anew. “I... assumed I’d be calling Pete,” she says, to at least go with truth.
“Interesting assumption. Perhaps necessary, if you believe I’ll be insufficient.”
Myka’s impulse is to reassure: “More than sufficient—you’re necessary,” she would shout, or better yet, whisper. Instead, because Helena’s tone is neutral—is she in actuality indifferent?—she falls into a defensive, businesslike crouch, offering only implicit denial of the premise of Helena’s statement. “Let’s head for the accounting firm,” she says, internally cursing herself.
Cursing, but also justifying: Helena is here as backup, thanks to Claudia’s cleverness, and Myka should not assume (speaking of assumptions) that she even wants to be here. All focus should be on retrieving the artifact. Certainly on that and not on Myka’s (honestly) predictably overexcited blood.
She tries to concentrate on Claudia’s advice (while at the same time trying not to resent her success at being cryptic about it): what’s a bonus, really? Helena’s presence, the sight of her, the apprehending of her impatience, the experience of blood: whatever else may happen, these have been—must be—are!—the bonus.
****
The cab ride is quiet. Myka’s resolve to think only of backup and bonus is dissolving by the second, and she lets words reach her tongue that might start a conversation with Helena about things... but those words don’t escape her lips, for a strand of formality seems to be stiffening Helena’s spine. Does she know how Myka cherished her impatience? Is she attempting to discourage such adoration?
Myka, in regret and relief, follows that more-strict lead.
That’s a bonus too, though, for it turns the ride into unpressured, liminal time, perfect for simply basking in presence. It’s best, Myka is now thinking, to treat this reunion as something that was of course going to have happened. For backup or other professional purposes. Despite the fact that it’s the thank-god fulfillment of recurring, desperate dreams.
However: at one point in the traffic-backed silence, Helena, completely unprompted, turns and smiles at Myka.
Myka smiles back.
It’s a previously missing puzzle-piece slotting into place... yet in its aftermath, Myka finds herself having to push with force against a will to worry over other missing pieces; in particular, she must fight the fret-intensive futility of trying to count them.
****
They find the accounting firm’s lobby spacious but quiet—holiday-low staffing, presumably. Myka asks the receptionist, “Is there someone we can talk to about end-of-year bonuses? Also penalties?”
“I’m a temp,” says the young man. His tone suggests it’s his answer to every query... but then he adds, very quietly, “Unofficially, there’s this one guy...”
That has the ring of “artifact,” so Myka nods, encouraging him.
“Super-vocal about his paycheck the other day. How tiny it was. I mean, he’s the kind of guy you might have theories about what else is tiny, but I—”
“Who was that?” Myka interrupts, even as she feels Helena’s readiness to laugh. Mr. Super-vocal is thus probably not a wielder of an artifact; more likely, one of that wielder’s... victims?
“Bob,” the temp says. “I’m sure he’s got a last name, and I’m sure he thinks everybody should call him ‘Mr. Lastname,’ but my care level? Anyway he’s down the hall—one of the only ones in the farm today. Spite-working. Maybe on his anti-everything manifesto.”
“Down the hall” turns out to be a vast expanse of cubicles: definitely a farm.
Myka says to Helena, “Follow my lead?”
“Always,” Helena says.
It’s a tonally sincere utterance—and in that, admirable—but it’s also manifestly untrue; nevertheless, Myka’s blood decides to believe it, to recognize it as another puzzle-piece. I really need to function, Myka tries to explain to her interior. So if we could climb down just a couple rungs. Like to the cab-ride level, maybe?
Her body refuses the agreement.
Of course.
The occupant of the first inhabited cubicle they find is an over-coiffed middle-aged man who clearly spends far too much time in tanning booths. He’s typing aggressively, as if the force of his keystrokes will power his message. His manifesto?
“Are you Bob?” Myka asks him.
“You better be here about my money,” obviously-Bob says, clearly spoiling for a fight.
Myka finds his demand incongruous—his job has to do with other people’s money, and Myka and Helena are manifestly other people. Who could have money. Fred or otherwise.
“In a way,” she says. She follows up with “We’re from the IRS,” and it’s never not funny for that to be useful. Bob winces, as if she's about to strike him. Also never not funny. “We’ve noted some suspicious discrepancies in end-of-year reporting.”
“You have?” Bob asks. Now he’s avid rather than confrontational.
“Looks like some overreporting. Also underreporting. So you see our concern, particularly about effects on withholding.” She is making this up, as she generally does whenever she has to go actual IRS on someone. Read up on tax law, she reminds herself, as she generally does every time. Not that she’ll ever have the leisure to do that... “What we need to find out is whether it was in error, or if it warrants a full investigation.”
“Nancy Sullivan,” he says, with contempt, the name itself a curse. “She’s the one you should investigate, and then send straight to jail. She’s always been a witch about year-end, but now? On steroids. Talking about making her list, threatening to mark down people she doesn’t like, including yours truly, as naughty... and then we got our paychecks, and somehow she did it! No idea how she managed to push that garbage through, but I swear you better get her up on some kind of charges!”
He rises abruptly, clutching a slip of paper; his chair topples over behind him. He shoves the paper in Myka’s direction, his knuckles nearing her astonished nose—but in the instant before contact, Helena intervenes, her arm blocking his, stopping his forward motion.
Backup.
Helena plucks the paper from his pushy hand. “And what’s this?” she asks.
A pretty minimal manifesto, Myka thinks initially. But then she replays his screed in her head, and his babbling about Nancy Sullivan resolves into meaningful references; struck by the realization, she very nearly misses his next statement: “My pay stub. She can’t just do this.”
Helena says, “Of course not.” She’s soothing him, her voice a faux-caress. It’s enough to tempt Myka to act out, just to hear it directed her way, even as Helena continues, “But we understand some of your colleagues, to the contrary, received large bonuses.”
His “tanned” skin darkens further. “Guess she thought they were nice. To her. Suck-ups.”
Mya looks a Find out anything else that’s relevant at Helena, who nods. Retreating back to the pre-cubicle hallway—relieved that her nose is intact—she Farnsworths Claudia. She skips the pleasantries, starting with, “A very disgruntled employee says the woman who signs off on bonuses was making a list.”
Claudia chortles. “You’re hilarious. Was she checking it twice?”
“This is my point. We don’t know exactly what we’re dealing with, not yet, but I bet that’s the crux.”
“I should’ve known you weren’t aiming for hilarity. So you really think this is some Santa thing?”
“No. I’m saying words about lists because I think it’s a grocery thing.” Myka wants to shake her fist at the heavens and every deity who occupies it. Occupies them. All the heavens. “Of course I think it’s a Santa thing! I also think it’s Pete’s fault somehow.”
“Just because it’s Christmas? C’mon.”
“Christmas and Ohio?” Myka snorts. “You c’mon. I don’t believe in coincidence.”
“Maybe you should though. For peace of mind?”
“That’s another thing I don’t believe in. Just see if you can find anything about a Santa’s-list artifact, would you?”
“Roger. By the way, how do you like your backup?” She chortles again and disconnects.
“I like my backup like I like the sunrise,” Myka tells the blank Farnsworth screen.
“What about the sunrise?” Helena asks from directly behind her.
Myka wishes the sound of her voice were either more or less startling. She wishes also that she knew exactly how much overhearing had occurred.
“It’s inevitable,” she sighs.
In response, Helena blinks.
They take the elevator to Nancy Sullivan’s office.
In that elevator, which is aggressively mirrored, Myka can’t help but glance repeatedly at herself. So many reflections. You called this into being, thinking about Alice’s mirror before, she accuses. She tries not to focus on how her hair could really stand to be more controlled... she’d focus on Helena instead, but who knows how that would be received? Instead she allows herself one glance, then looks down.
She likes being on the elevator with Helena, though; it’s a space of relative privacy, like the cab. Have they ever before been on an elevator together? Alone or otherwise? She runs through their interactions, fast-forwarding from the Wells house to D.C., Tamalpais to Moscow, Yellowstone, Colorado Springs, Ohio (here Myka trips over the fact that Helena’ s now been to Ohio twice, if only once in physical form), Pittsburgh, Hong Kong...
The review—the speed with which she can conduct it—reminds her of how limited that time has been, so: an elevator ride. Yet another bonus.
“That fellow,” Helena remarks, and Myka looks up again; their eyes meet in the mirror of the elevator’s doors. It’s uncanny, as if they’re both holograms, so Myka turns her body toward Helena, who meets Myka’s actual eyes and continues, “He attempted to make a lewd joke about his willingness and ability to be naughty when it’s called for. I pretended not to understand.”
Myka can’t help it: she snorts. “I bet he didn’t buy that for a second.”
“I have the ability to perform ‘prim’ when it’s called for,” Helena says, and Myka has to acknowledge that statement as good evidence of itself. Then Helena’s face reshapes into a devilish grin as she says, “In a slightly different vein, his quailing at those three letters with which you assailed him? Hilarious.”
“Letters?” A little perverse-quirk makes Myka want to hear Helena say them, though she’s probably not pulling off “disingenuous” in making the request.
Helena seems fine with the perversity, for she obliges: “I,” she begins, then draws out “Aaaaare.” Then, after a beat: “Esssss.”
Myka now herself feels assailed—by how right Helena’s reading her. She tries to step it down with, “I wasn’t aiming for hilarity. I never do. Claudia can vouch.” But she does spend a little moment thinking about the context of that previous assailing: we’re from the IRS. We are here, together, from an agency. We, together, represent. It isn’t by any means everything Myka would have wanted... but it’s something: part of this bonus. “Fred,” she says, sotto voce.
The office they’re seeking is on the building’s highest floor, suggestive of Nancy Sullivan’s bonus-approving rank; it features several large windows, one of which affords the office a view of the hallway, and vice versa. Through it, Myka and Helena watch a woman, presumably that powerful Nancy Sullivan, writing with a quill-esque pen.
“It’s the pen,” Myka says, because it has to be. “It’s always the stupid pen.”
“Always?” That’s unusually tentative, like Helena’s trying not to step.
“Okay, once,” Myka concedes. “My dad and Poe and a pen, and as a result I’ve developed a severe aversion to those quill things.”
Helena takes a beat. Then: “I never liked feather pens.”
“Are you just saying that,” Myka says, because she might be, and she might admit it, and that might be good or bad or something else Myka has no way of evaluating. Why does Helena say words like this? And for that matter, why does Myka keep spending her limited time on this planet trying to parse them?
“Yes? In that I’ve... said it?”
That really didn’t help with any of the whys. “I mean, just to make me feel better?”
Helena shrugs. “The fact is, today’s ballpoints et cetera are far more reliable. Does that make you feel better?”
She’s playing at being obtuse—surely that’s for a reason? But Myka has no time to wonder further, for Helena is knocking on the office door and opening it without waiting for an invitation, and the real retrieval is underway.
Myka flashes her badge. “I’m Agent Myka Bering, and this is Helena Wells. We’re from the IRS.” She glances at Helena—all these glances!—and gets a small smirk in response.
Rather than introducing herself, the woman says, “Really? I bet that’s not true.”
“Why?” Myka asks. Have she and Helena, over the course of the elevator ride, lost their ability to perform “official” correctly?
“I have a feeling you’re here for this,” Nancy Sullivan says, and she lofts the pen, waving it like a wand. “Mostly because I also have a feeling that I want to close my fist around it, punch my way past both of you, and make my escape.”
Well. “That’s self-aware,” Myka says. “Unusually so.”
“Thank you? Although it’s less self-awareness than kind of a... sixth sense.”
Helena raises an eyebrow at Myka. “Sixth sense aside, we appreciate your good sense to refrain from attempting to punch your way past us. That would have ended poorly.”
“I wish I’d had the good sense not to use this pen,” Nancy Sullivan says.
“Is there a reason for your wish?” Helena asks. She sounds, to Myka’s ears at least, like a recently summoned, slightly flummoxed genie.
“Because of how much I liked using it—particularly when I realized nobody was going to question anything. I signed off on all these orders, and it was like...” she trails off. Then she concludes, “Magic.”
To keep her talking, Myka prompts, “Was it?”
“Having the power to reward good people has been fantastic,” Nancy Sullivan continues, “but penalizing the awful ones? I mean I’ve sort of resented feeling compelled to use the word ‘naughty’ about them, because that’s way out of character for me. But other than that? Utterly spectacular.”
“Bob,” Helena suggests.
“Oh, god, you met him?”
Helena offers a dry “Alas.”
Nancy Sullivan’s smile is as dry as Helena’s tone, astringently vindictive. “I could not have been more thrilled to hit him and everybody like him where it hurt... I admit I’ve always been kind of judgmental, but wielding this pen? Intensified. Like, the hates are more. In particular, the hates are more. I’m not saying the Bobs of this company didn’t deserve what I did, but I feel it more. Punishment. It’s satisfying, but also weirdly costly. Grinch-in-reverse costly.”
That’s a little on the nose. Myka glances at Helena again, because the satisfactions of punishment, of judgment, even of hate, are among the things they will need to talk about. Maybe. Someday. If they are to have a someday that is theirs... if that is even possible after so much time and tribulation... Myka lets the glance grow into a gaze, a resting regard, and it stays that way until Helena, too, glances, with the result then that their eyes meet and lock... such a clasp, Myka feels, could ground that potential, and potentially necessary, talk of things, if only they were not in the middle of a retrieval...
...which makes Myka think. Why are they in the middle of a retrieval?
“I wish I didn’t feel like I need to articulate this, but where did you get the pen?” she asks. Because she has a niggling sense of something larger happening, something beyond her grasp. Nevertheless, it is not—repeat, not—a vibe.
Fine. It might be a vibe.
“My cousin gave it to me,” says Nancy Sullivan.
“Your cousin,” Myka says. “Whose name is?” Now she’s knows what’s coming, and that has nothing to do with a vibe: no, it is entirely deduction based on experience.
“Pete Lattimer.”
TBC
#bering and wells#warehouse 13#fanfic#Bonus#holiday (but not Gift Exchange)#proceeding at a vaguely nonzero speed#being left in the dust by snails and tortoises#but I do still love a Myka who fights with herself about who deserves what (and why)#and of course a Helena who can be reasonably inferred to do the same#struggling against the graceful acceptance of gifts#whatever form they take
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
Somebody other than me cares!
For only the second time in the last decade or more, my personal obsession is in the news and I'm incredibly excited. "Below the fold," in old newspaper jargon, but at least somebody's trying to do something and some newspapers noticed. When you're as starved for validation as I am, it only takes that much attention to excite me.
Amudalat Ajasa and Carolyn Van Houten, "Lead paint upended this boy’s life. Now the EPA is trying to eliminate the threat. The Environmental Protection Agency is about to issue strict limits on lead dust, which poses a threat to millions of children across the United States," Washington Post. Oct 19, 2024 (non-paywall link)
Lead was used as a paint additive from Victorian times up until the late 1970s for a couple of reasons. It made a bright white pigment that didn't fade quickly, it was shiny, and most importantly to the Victorians, it tolerated harsh cleaning chemicals well, which they thought was important to reducing the spread of disease.
(On a local note for here in St. Louis MO USA, it also almost single-handedly propped up the local economy in this town for that whole century, thanks to the huge lead mines south of town and our ability to export products to the whole world via our port on the Mississippi river. Almost all of the abandoned factory and warehouse buildings down here in South St. Louis are contaminated former lead-paint businesses.)
Lead paint though has an even bigger problem than lead pipes, though: over time, it starts shedding lead dust, and children are incredibly vulnerable to lead dust, breathing it in and/or swallowing it. And it takes very little lead dust to permanently damage a growing mind, destroying the parts of the brain that control impulses and the ones that down-regulate emotions.
This is why lead paint was outlawed in the late 1970s. But there was no law requiring it to be removed from (frankly, nearly all) surfaces. Instead, there was a voluntary lead abatement program, and even it only applied to residential property. Homeowners and apartment owners could borrow money from the nearest S&L, pay contractors to rip out and replace all the lead-dust tainted windows, carpets, plaster walls, and so forth and replace them with clean new vinyl-clad or latex-painted bits. They could then submit the receipts with their taxes and get a 100% refundable tax credit.
But they weren't able to make it mandatory because of intense lobbying by openly-racist slumlords, who didn't want to lead abate their properties even it was free because that's telling them what to do with their property, who didn't think their black tenants "deserved" refurbished apartments. That's also why it's illegal to disclose, in sales or in rental contracts, that your property has been through lead abatement; doing so is "unfair" to those '70s slumlords.
And besides, Reagan canceled the whole program halfway though his first term. To bend over backwards to be fair to Reagan, they weren't still getting many applications; everybody who was going to do so voluntarily already had. (Free money for home improvements has that effect.)
About a decade ago, a Reuters reporter used FOIA to demand state health departments turn over their records on childhood lead testing. Almost half of them don't keep any. Most only track it at the state level or maybe county level. Missouri's one of the only states that tracks it to the census-tract level, tracks where kids who are lead poisoned live to within a couple of blocks. And the map of apartments that didn't go through lead abatement, here in Missouri, perfectly maps onto the homicide data.
As someone who was pretty badly lead poisoned as a teenager myself, and as someone who's spent most of his life living in or near lead-poisoned apartments, I'm obsessed with this and ever since the Reuters article came out I've been begging every politician or candidate I interact with to bring back the late '70s lead abatement tax credit and this time make it mandatory to test before selling or leasing a home. Even when St. Louis, with its nominally, mostly progressive mayor got huge uncommitted funds dumped on her, from ARPA and from the Rams-relocation-fraud settlement, I couldn't get any politician to care about this. Their constituents weren't demanding it, so it couldn't be done.
The Washington Post reported, today, that the US Environmental Protection Agency has proposed a rule to do just that. No tax credit provision, so they're being fought tooth and nail by people who don't want to make property sellers and landlords pay for it out of pocket, but the proposed rule is on the docket, potentially to take effect mid next year. Somebody other than me noticed. Somebody other than me cares.
If you are like the average person (to my distress) the main thing you want to know is "what can I do to protect myself or my kids?"
This is a shitty way to think because let me tell you, if your kid grows up on the same block as a lead-poisoned kid, your kid is going to grow up with C-PTSD from the resulting violence. Your kids aren't safe until everybody's kids are safe.
I didn't convince you? You've given up on keeping everybody else's kids safe, too?
If you have a painted surface anywhere on your property that existed prior to 1976, you should assume that there is lead paint on it. Older chain-link fences almost certainly. Wooden single-pane windows, 100% likely. If you have plaster, instead of drywall, interior walls in your house, then neither the walls nor the floorboards nor the carpets are safe. They will tell you these surfaces can be rendered safe by painting over them with latex paint; anybody who tells you this is whistling past the graveyard.
Do not have or raise kids in a house or apartment like that. Either abate the lead or move. Yes, even if it's more expensive; the alternative is to raise a child who may never work and has a high likelihood of spending most of their life in and out of jail.
If it's too late for that, and your child is already lead poisoned, don't give up hope entirely, but understand that the interventions that show promise for such kids are hard to find and aren't 100% reliable.
The most important thing you can do is investigate the concept of "trauma-informed schools," and demand, as part of your child's IEP, that his teacher and any associated staff get trauma-informed schooling trained. (Your kid will not be the only one who benefits.)
Children with profoundly impaired impulse control and/or profoundly impaired emotional down-regulation skills can be taught to do better, but that requires that they be given the extra time it will take them to do so, and the privacy, and the calm quiet space, especially when they're very young and just learning. Their brains don't do this naturally, so they don't do them quickly; hold them to the same standard of behavior as everybody else but until they spend a decade or more practicing and grow up more, after you remind them, give them enough time to obey.
But believe me when I tell you this: lead abatement and behavioral education are cheaper and better than prison.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Apple has been granted a patent for “identity recognition utilising face-associated body characteristics,” which combines facial recognition technology with other body characteristics to identify people even when their faces are not visible to the camera.
Apple’s patent, filed in May 2022 and granted on 26 November 2024, describes a system that associates facial recognition with other body characteristics such as clothing, gait or gesture to recognise certain people.
The system works by linking a gallery of “body croppings” such as torso, arms or legs with their face biometrics, then comparing the data with a live video feed, and proceeds in a stepped approach to identify face, body parts and physical characteristics, which include body shape, skin colour, or the texture or colour of clothing.
The resulting data constitutes a cluster of “bodyprints” which can be assigned a confidence score against a person’s faceprint and other characteristics, with storage periods as brief as 24 hours for certain identifiers like clothing.
The system can recognise people based on their body characteristics, even if they are wearing different clothes, and can re-register their clothes periodically to maintain accurate identification.
“It all appears to add up to a smart camera system that knows a person’s face and walk but re-registers his clothes in the morning so that it is able to recognise him on his way home even if it can’t see his face because it knows his Hawaiian shirt,” Biometric Update reported.
Although the patent is primarily directed to performing identity recognition in a home environment setting, Apple notes that it should not be construed as being limited to this setting.
The technology can be used in various environments, including homes, office buildings, warehouses, parking lots, and public parks. And although Apple doesn’t say so, we shouldn’t be surprised if it turns up in applications in law enforcement, border control, intelligence, access management and event security.
As Biometric Update notes, Apple patents many technologies that it never makes but its interest in a smart AI camera that performs broad identity recognition is understandable given the growing markets for AI and facial authentication.
The above is a summary of the article ‘Apple patent uses FRT with ‘body data’ so cameras can ID people without seeing faces’ published by Biometric Update. Read the full article HERE.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
I've named the most common jobs I can think of! I want to see how many people have worked each of these. Vote the one you did the longest, or was the most notable, but only mark "none" if literally no job you have ever had applies at all.
I realize the things I grouped weren't all that related, but I had a limited number of spaces to cover.. all jobs lol. So just vote the closest applicable option!
Tell me what jobs I should have included! I'd love to hear from you.
Reblog for sample size :)
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
SERVO DISTANCE INDICATOR USING ARDUINO UNO
INTRODUCTION
Distance measurement is a fundamental concept in various fields, including robotics, automation, and security systems. One common and efficient way to by emitting sound waves and calculating the time it takes for the waves to reflect back from an object, allowing accurate measurement of distance without physical contact.
In this project, we will use an HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor in conjunction with an Arduino microcontroller to measure the distance between the sensor and an object. The sensor emits ultrasonic waves and measures the time it takes for the waves to return after reflecting off the object. By using the speed of sound and the time measured, the distance is calculated. This simple yet powerful setup can be applied in a variety of real-world applications such as obstacle detection in robots, parking assistance systems, and automatic door operations.

WORKING PRINCIPLE
1. Servo Movement: The servo motor rotates to different angles (0° to 180°). The ultrasonic sensor is mounted on top of the servo and moves with it.
2. Distance Measurement: At each position, the ultrasonic sensor sends out an ultrasonic pulse and waits for the echo to return after hitting an object. The Arduino records the time taken for the echo to return.
3. Distance Calculation: The Arduino calculates the distance to the object based on the time recorded and the speed of sound (0.0343 cm/µs).
4. Servo as Indicator: The servo motor's position provides a physical indication of the direction of the detected object. As the servo moves across a range of Image map out objects in different directions based on distance.
5. Visual Output: The Arduino can also send the distance and angle data to the serial monitor, creating a real-time visual representation of the detected object positions.
APPLICATIONS
1. Autonomous Robots and Vehicles
2. Radar Systems
3. Parking Assistance
4. Security Systems
5. Environmental Scanning in Drones
6. Warehouse Management and Automation
7. Industrial Automation
8. Robotic Arm Guidance
9. Collision Avoidance in UAVs/Robots
10.Interactive Displays or Art Installations
11.Smart Doors and Gates
CONCLUSION
The Servo Distance Indicator Project successfully demonstrates the integration of an ultrasonic sensor and a servo motor to create an effective distance measurement an object, the project provides real-time feedback through the movement of a servo motor, which indicates the measured distance via a visual representation.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Data Warehouse Services in Basking Ridge NJ
#quellsoft#Data Warehouse Services in Basking Ridge NJ#Data Warehouse Services#Cloud Applications in Basking Ridge NJ#Data Integration in Basking Ridge NJ#Cloud Computing in Basking Ridge NJ#Cloud Data Warehousing in Basking Ridge NJ
0 notes
Text
Warehouse Buzzer System
How Electronic Message Boards Assist In Updating

Electronic message boards are fairly prevalent today, and their usage seems to be proliferating. Message boards in electronic kind properly interact swiftly upgraded company memoranda, final timetable modifications, and marketing, three fairly various applications providing one an idea of the breadth that this medium has gotten to. Herein we explore the phenomenon both generally and in regards to the power released when incorporated with an integrated clock system.
Electronic message boards derive from a lengthy background of open-air communication making use of indicators, billboards, marquees, and so on. Trick attributes were the layouts utilized and the feedback time for updating info. The most usual style entailed drawing on comprehensive personality collections, containing letters, numbers, and spelling, to create words, hanging them from hooks or resting them on wooden slats.
Posts were changed by hand, and updates were thus irregular. In time, updating was improved and somewhat automated using electronic control, such as seen with old baseball park scoreboards.
However, there was still the danger of lacking specific characters and being rendered unable to display all words in your message. This problem was addressed when the dot matrix selection was created, which stood for any type of character (in any type of typeface)-- also graphics-- with a rectangular pattern of on-or-off dots. These could be published on paper, yet a lot more effective was to present them in grids of light bulbs or on a screen.
Mapping formulas converted text into ranges of dots virtually instantaneously, and while drivers entered on a console, messages scrolled across the screen in essentially live. This system still required manual work, however the display screen tool was much easier to read, new, and updatable in a matter of moments. Whence the birth of electronic message boards that utilized light bulbs as the dots, or pixels.
Early light bulbs were incandescent, and were really the only choice; nonetheless, they had brief life-spans and prone to failing from shock. By the millenium, light producing diodes (LED) were a fully grown innovation and available in several shades, including white. Additionally, they outlived incandescent light bulbs by approximately 50 times, were not so breakable, and rapidly came to be the recommended part for message boards.
In time developers got extra creative with the tool and wanted to have more than one "on" shade to deal with. LEDs can fulfill this desire with their 3-in-1 mix of the 3 primary colors to synthesize white light; by choosing different sub-combinations you can obtain 7 various shades.
At some point, upgrading had to transition out of its humble manual origins. Now, textual info can be gotten in real time or gotten from data sources, and software is utilized to map the information right into matrices of (color-coded) dots that get buffered and presented quickly, effortlessly, and effortlessly. Graphics can be incorporated if they are mapped in advance.
Therefore, the modern digital boards are essentially automated, though there are provisions for bypassing scheduled programs with brand-new content in emergencies. Synchronous timekeeping systems manage everything.
An intriguing advancement is the integration of sound signals with the visual information being displayed on a sign in either textual or visual kind. It is popular that a close coordination of both kinds of sensuous stimulations has a tendency to get the message throughout many successfully. It's not a combination of both elements into tune, yet rather the use of sounds (bells, tones, whistles) as focus grabbers to change emphasis of the target market to what the board is showing, whether it be information or other timely information. synchronized clocks for hospitals
The world has actually expanded tired with fixed messaging in regards to both web content and style. Things need to be vibrant to sign up, and this needs constant educational updates. With this article we have seen exactly how electronic message boards promote updating.
youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of Business Intelligence: Trends and Technologies Shaping Decision Support Systems - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/the-future-of-business-intelligence-trends-and-technologies-shaping-decision-support-systems-technology-org/
The Future of Business Intelligence: Trends and Technologies Shaping Decision Support Systems - Technology Org
Business intelligence (BI) is an umbrella term for technologies, processes, and analytics that help companies understand the state of their business. BI has evolved from traditional data warehouse systems, which were primarily used to capture and store data. Today’s technology has made it possible for business users to take action on insights with more agility than ever before. In this guide, we’ll explore how BI is evolving and why you should consider adopting a modern approach to decision support systems (DSS).
Working with business clients – illustrative photo. Image credit: Ronald Candonga via Pixabay, free license
The Need for Change
Business intelligence (BI) is not a new concept. It has been around for many years, but the business landscape has changed dramatically over that time. The need for BI is greater than ever before because of these changes in the business landscape:
Data is everywhere. Organizations are generating more data than they know what to do with it; this makes it difficult for them to make decisions based on incomplete information or outdated data
New technologies have emerged that allow organizations to collect and analyze information faster than ever before, which means they need better tools for making sense of all their new data sources
The way people think about technology has changed due to advances in mobile devices and social media networks like Facebook and Twitter
Enter Business Dashboards
Business dashboards are a way to visualize data in a way that is easy to understand. They are used to monitor performance, track progress, and make decisions and they can be used with data from different sources. Business dashboards are being adopted by executives and managers who want real-time access to their company’s KPIs (key performance indicators). Analysts also use them because they can get the information they need through one interface rather than having multiple applications open at once or searching through multiple reports on their desktops or laptops.
Dashboards for business are not just a technological convenience; they represent a strategic advantage in the fast-paced landscape of contemporary decision-making.
Business intelligence software has become more sophisticated over time as it’s been able to handle larger amounts of information at once while still providing users with simple ways of accessing that information quickly and easily when needed most likely when there’s an urgent decision that needs making right away!
Analysts are using business intelligence software more and more to help them make decisions. This is because the software can handle large amounts of data without slowing down, making it easier for analysts to access critical information when they need it most. Business dashboards are one way that companies can use BI tools; they provide real-time access to KPIs so users don’t have to spend time searching through reports on their desktops or laptops.
Key Benefits of Business Dashboards
Business dashboards are an effective way to make decisions faster and more effectively. They can help you increase productivity, reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and even increase employee productivity.
Improve decision-making: Business dashboards help you make better decisions by providing you with real-time data that’s easy to understand.
Reduce stress levels: Dashboards can be used by anyone from entry-level employees up through executives in your organization so everyone can access information about their area of expertise at any given time without having any prior training on how BI tools work or what they do for businesses overall
Improve employee engagement: Dashboards can help increase employee engagement by providing them with a better understanding of the company’s overall performance. This leads to increased productivity and makes employees feel like their work is making a difference in the world.
Implementation Process
Before you start on a BI project, it’s important to define the problem. If you don’t know what problem you’re trying to solve or how it will benefit your organization, then any solution is going to be flawed. You need to know what goals you want to achieve and why they’re important before starting on any solutions.
Once these questions have been answered and goals are set, then comes the fun part: figuring out how exactly we’re going about achieving them! This step is where many people fall into trouble; they get too caught up in what other people think their goals should be instead of focusing on their ambitions and abilities (and no one knows better than YOU what kind of success would make YOU happy). Set ambitious but realistic expectations for yourself if it takes three months instead of six months or costs $100 instead of $1000 per month (or whatever), don’t worry about those things just focus on getting started today with whatever small step(s) seem feasible right now rather than waiting until everything falls perfectly into place before taking action!
Don’t be discouraged if you have to make some changes along the way; just take it as an opportunity to learn from your mistakes and adjust accordingly.
Conclusion
If you’re looking to make the most of your business intelligence, it’s time to consider a dashboard. The benefits of this technology are clear, and there are many tools available to help you implement it.
#Analytics#applications#approach#bi#bi tools#Business#Business Intelligence#Capture#change#Companies#dashboard#data#data warehouse#decision support#devices#easy#employee engagement#employee productivity#employees#executives#Facebook#Fintech news#Future#how#insights#intelligence#it#Landscape#laptops#Learn
0 notes
Text
Data warehousing solution
Unlocking the Power of Data Warehousing: A Key to Smarter Decision-Making
In today's data-driven world, businesses need to make smarter, faster, and more informed decisions. But how can companies achieve this? One powerful tool that plays a crucial role in managing vast amounts of data is data warehousing. In this blog, we’ll explore what data warehousing is, its benefits, and how it can help organizations make better business decisions.
What is Data Warehousing?
At its core, data warehousing refers to the process of collecting, storing, and managing large volumes of data from different sources in a central repository. The data warehouse serves as a consolidated platform where all organizational data—whether from internal systems, third-party applications, or external sources—can be stored, processed, and analyzed.
A data warehouse is designed to support query and analysis operations, making it easier to generate business intelligence (BI) reports, perform complex data analysis, and derive insights for better decision-making. Data warehouses are typically used for historical data analysis, as they store data from multiple time periods to identify trends, patterns, and changes over time.
Key Components of a Data Warehouse
To understand the full functionality of a data warehouse, it's helpful to know its primary components:
Data Sources: These are the various systems and platforms where data is generated, such as transactional databases, CRM systems, or external data feeds.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): This is the process by which data is extracted from different sources, transformed into a consistent format, and loaded into the warehouse.
Data Warehouse Storage: The central repository where cleaned, structured data is stored. This can be in the form of a relational database or a cloud-based storage system, depending on the organization’s needs.
OLAP (Online Analytical Processing): This allows for complex querying and analysis, enabling users to create multidimensional data models, perform ad-hoc queries, and generate reports.
BI Tools and Dashboards: These tools provide the interfaces that enable users to interact with the data warehouse, such as through reports, dashboards, and data visualizations.
Benefits of Data Warehousing
Improved Decision-Making: With data stored in a single, organized location, businesses can make decisions based on accurate, up-to-date, and complete information. Real-time analytics and reporting capabilities ensure that business leaders can take swift action.
Consolidation of Data: Instead of sifting through multiple databases or systems, employees can access all relevant data from one location. This eliminates redundancy and reduces the complexity of managing data from various departments or sources.
Historical Analysis: Data warehouses typically store historical data, making it possible to analyze long-term trends and patterns. This helps businesses understand customer behavior, market fluctuations, and performance over time.
Better Reporting: By using BI tools integrated with the data warehouse, businesses can generate accurate reports on key metrics. This is crucial for monitoring performance, tracking KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), and improving strategic planning.
Scalability: As businesses grow, so does the volume of data they collect. Data warehouses are designed to scale easily, handling increasing data loads without compromising performance.
Enhanced Data Quality: Through the ETL process, data is cleaned, transformed, and standardized. This means the data stored in the warehouse is of high quality—consistent, accurate, and free of errors.
Types of Data Warehouses
There are different types of data warehouses, depending on how they are set up and utilized:
Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW): An EDW is a central data repository for an entire organization, allowing access to data from all departments or business units.
Operational Data Store (ODS): This is a type of data warehouse that is used for storing real-time transactional data for short-term reporting. An ODS typically holds data that is updated frequently.
Data Mart: A data mart is a subset of a data warehouse focused on a specific department, business unit, or subject. For example, a marketing data mart might contain data relevant to marketing operations.
Cloud Data Warehouse: With the rise of cloud computing, cloud-based data warehouses like Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, and Snowflake have become increasingly popular. These platforms allow businesses to scale their data infrastructure without investing in physical hardware.
How Data Warehousing Drives Business Intelligence
The purpose of a data warehouse is not just to store data, but to enable businesses to extract valuable insights. By organizing and analyzing data, businesses can uncover trends, customer preferences, and operational inefficiencies. Some of the ways in which data warehousing supports business intelligence include:
Customer Segmentation: Companies can analyze data to segment customers based on behavior, demographics, or purchasing patterns, leading to better-targeted marketing efforts.
Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical data, businesses can forecast trends and predict future outcomes, such as sales, inventory needs, and staffing levels.
Improved Operational Efficiency: With data-driven insights, businesses can streamline processes, optimize supply chains, and reduce costs. For example, identifying inventory shortages or surplus can help optimize stock levels.
Challenges in Data Warehousing
While the benefits of data warehousing are clear, there are some challenges to consider:
Complexity of Implementation: Setting up a data warehouse can be a complex and time-consuming process, requiring expertise in database management, ETL processes, and BI tools.
Data Integration: Integrating data from various sources with differing formats can be challenging, especially when dealing with legacy systems or unstructured data.
Cost: Building and maintaining a data warehouse can be expensive, particularly when managing large volumes of data. However, the investment is often worth it in terms of the business value generated.
Security: With the consolidation of sensitive data in one place, data security becomes critical. Organizations need robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
The Future of Data Warehousing
The world of data warehousing is constantly evolving. With advancements in cloud technology, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, businesses are now able to handle larger datasets, perform more sophisticated analyses, and automate key processes.
As companies increasingly embrace the concept of a "data-driven culture," the need for powerful data warehousing solutions will continue to grow. The integration of AI-driven analytics, real-time data processing, and more intuitive BI tools will only further enhance the value of data warehouses in the years to come.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced, data-centric world, having access to accurate, high-quality data is crucial for making informed business decisions. A robust data warehousing solution enables businesses to consolidate, analyze, and extract valuable insights from their data, driving smarter decision-making across all departments. While building a data warehouse comes with challenges, the benefits—improved efficiency, better decision-making, and enhanced business intelligence—make it an essential tool for modern organizations.
You said:
blog for Data warehousing
ChatGPT said:
Title: Data Warehousing: The Backbone of Data-Driven Decision Making
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the ability to make data-driven decisions quickly is paramount. However, to leverage data effectively, companies need more than just raw data. They need a centralized, structured system that allows them to store, manage, and analyze data seamlessly. This is where data warehousing comes into play.
Data warehousing has become the cornerstone of modern business intelligence (BI) systems, enabling organizations to unlock valuable insights from vast amounts of data. In this blog, we’ll explore what data warehousing is, why it’s important, and how it drives smarter decision-making.
What is Data Warehousing?
At its core, data warehousing refers to the process of collecting and storing data from various sources into a centralized system where it can be easily accessed and analyzed. Unlike traditional databases, which are optimized for transactional operations (i.e., data entry, updating), data warehouses are designed specifically for complex queries, reporting, and data analysis.
A data warehouse consolidates data from various sources—such as customer information systems, financial systems, and even external data feeds—into a single repository. The data is then structured and organized in a way that supports business intelligence (BI) tools, enabling organizations to generate reports, create dashboards, and gain actionable insights.
Key Components of a Data Warehouse
Data Sources: These are the different systems or applications that generate data. Examples include CRM systems, ERP systems, external APIs, and transactional databases.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): This is the process by which data is pulled from different sources (Extract), cleaned and converted into a usable format (Transform), and finally loaded into the data warehouse (Load).
Data Warehouse Storage: The actual repository where structured and organized data is stored. This could be in traditional relational databases or modern cloud-based storage platforms.
OLAP (Online Analytical Processing): OLAP tools enable users to run complex analytical queries on the data warehouse, creating reports, performing multidimensional analysis, and identifying trends.
Business Intelligence Tools: These tools are used to interact with the data warehouse, generate reports, visualize data, and help businesses make data-driven decisions.
Benefits of Data Warehousing
Improved Decision Making: By consolidating data into a single repository, decision-makers can access accurate, up-to-date information whenever they need it. This leads to more informed, faster decisions based on reliable data.
Data Consolidation: Instead of pulling data from multiple systems and trying to make sense of it, a data warehouse consolidates data from various sources into one place, eliminating the complexity of handling scattered information.
Historical Analysis: Data warehouses are typically designed to store large amounts of historical data. This allows businesses to analyze trends over time, providing valuable insights into long-term performance and market changes.
Increased Efficiency: With a data warehouse in place, organizations can automate their reporting and analytics processes. This means less time spent manually gathering data and more time focusing on analyzing it for actionable insights.
Better Reporting and Insights: By using data from a single, trusted source, businesses can produce consistent, accurate reports that reflect the true state of affairs. BI tools can transform raw data into meaningful visualizations, making it easier to understand complex trends.
Types of Data Warehouses
Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW): This is a centralized data warehouse that consolidates data across the entire organization. It’s used for comprehensive, organization-wide analysis and reporting.
Data Mart: A data mart is a subset of a data warehouse that focuses on specific business functions or departments. For example, a marketing data mart might contain only marketing-related data, making it easier for the marketing team to access relevant insights.
Operational Data Store (ODS): An ODS is a database that stores real-time data and is designed to support day-to-day operations. While a data warehouse is optimized for historical analysis, an ODS is used for operational reporting.
Cloud Data Warehouse: With the rise of cloud computing, cloud-based data warehouses like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake have become popular. These solutions offer scalable, cost-effective, and flexible alternatives to traditional on-premises data warehouses.
How Data Warehousing Supports Business Intelligence
A data warehouse acts as the foundation for business intelligence (BI) systems. BI tools, such as Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView, connect directly to the data warehouse, enabling users to query the data and generate insightful reports and visualizations.
For example, an e-commerce company can use its data warehouse to analyze customer behavior, sales trends, and inventory performance. The insights gathered from this analysis can inform marketing campaigns, pricing strategies, and inventory management decisions.
Here are some ways data warehousing drives BI and decision-making:
Customer Insights: By analyzing customer purchase patterns, organizations can better segment their audience and personalize marketing efforts.
Trend Analysis: Historical data allows companies to identify emerging trends, such as seasonal changes in demand or shifts in customer preferences.
Predictive Analytics: By leveraging machine learning models and historical data stored in the data warehouse, companies can forecast future trends, such as sales performance, product demand, and market behavior.
Operational Efficiency: A data warehouse can help identify inefficiencies in business operations, such as bottlenecks in supply chains or underperforming products.

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is Generative Physical AI? Why It Is Important?

What is Physical AI?
Autonomous robots can see, comprehend, and carry out intricate tasks in the actual (physical) environment with to physical artificial intelligence. Because of its capacity to produce ideas and actions to carry out, it is also sometimes referred to as “Generative physical AI.”
How Does Physical AI Work?
Models of generative AI Massive volumes of text and picture data, mostly from the Internet, are used to train huge language models like GPT and Llama. Although these AIs are very good at creating human language and abstract ideas, their understanding of the physical world and its laws is still somewhat restricted.
Current generative AI is expanded by Generative physical AI, which comprehends the spatial linkages and physical behavior of the three-dimensional environment in which the all inhabit. During the AI training process, this is accomplished by supplying extra data that includes details about the spatial connections and physical laws of the actual world.
Highly realistic computer simulations are used to create the 3D training data, which doubles as an AI training ground and data source.
A digital doppelganger of a location, such a factory, is the first step in physically-based data creation. Sensors and self-governing devices, such as robots, are introduced into this virtual environment. The sensors record different interactions, such as rigid body dynamics like movement and collisions or how light interacts in an environment, and simulations that replicate real-world situations are run.
What Function Does Reinforcement Learning Serve in Physical AI?
Reinforcement learning trains autonomous robots to perform in the real world by teaching them skills in a simulated environment. Through hundreds or even millions of trial-and-error, it enables self-governing robots to acquire abilities in a safe and efficient manner.
By rewarding a physical��AI model for doing desirable activities in the simulation, this learning approach helps the model continually adapt and become better. Autonomous robots gradually learn to respond correctly to novel circumstances and unanticipated obstacles via repeated reinforcement learning, readying them for real-world operations.
An autonomous machine may eventually acquire complex fine motor abilities required for practical tasks like packing boxes neatly, assisting in the construction of automobiles, or independently navigating settings.
Why is Physical AI Important?
Autonomous robots used to be unable to detect and comprehend their surroundings. However, Generative physical AI enables the construction and training of robots that can naturally interact with and adapt to their real-world environment.
Teams require strong, physics-based simulations that provide a secure, regulated setting for training autonomous machines in order to develop physical AI. This improves accessibility and utility in real-world applications by facilitating more natural interactions between people and machines, in addition to increasing the efficiency and accuracy of robots in carrying out complicated tasks.
Every business will undergo a transformation as Generative physical AI opens up new possibilities. For instance:
Robots: With physical AI, robots show notable improvements in their operating skills in a range of environments.
Using direct input from onboard sensors, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) in warehouses are able to traverse complicated settings and avoid impediments, including people.
Depending on how an item is positioned on a conveyor belt, manipulators may modify their grabbing position and strength, demonstrating both fine and gross motor abilities according to the object type.
This method helps surgical robots learn complex activities like stitching and threading needles, demonstrating the accuracy and versatility of Generative physical AI in teaching robots for particular tasks.
Autonomous Vehicles (AVs): AVs can make wise judgments in a variety of settings, from wide highways to metropolitan cityscapes, by using sensors to sense and comprehend their environment. By exposing AVs to physical AI, they may better identify people, react to traffic or weather, and change lanes on their own, efficiently adjusting to a variety of unforeseen situations.
Smart Spaces: Large interior areas like factories and warehouses, where everyday operations include a constant flow of people, cars, and robots, are becoming safer and more functional with to physical artificial intelligence. By monitoring several things and actions inside these areas, teams may improve dynamic route planning and maximize operational efficiency with the use of fixed cameras and sophisticated computer vision models. Additionally, they effectively see and comprehend large-scale, complicated settings, putting human safety first.
How Can You Get Started With Physical AI?
Using Generative physical AI to create the next generation of autonomous devices requires a coordinated effort from many specialized computers:
Construct a virtual 3D environment: A high-fidelity, physically based virtual environment is needed to reflect the actual world and provide synthetic data essential for training physical AI. In order to create these 3D worlds, developers can simply include RTX rendering and Universal Scene Description (OpenUSD) into their current software tools and simulation processes using the NVIDIA Omniverse platform of APIs, SDKs, and services.
NVIDIA OVX systems support this environment: Large-scale sceneries or data that are required for simulation or model training are also captured in this stage. fVDB, an extension of PyTorch that enables deep learning operations on large-scale 3D data, is a significant technical advancement that has made it possible for effective AI model training and inference with rich 3D datasets. It effectively represents features.
Create synthetic data: Custom synthetic data generation (SDG) pipelines may be constructed using the Omniverse Replicator SDK. Domain randomization is one of Replicator’s built-in features that lets you change a lot of the physical aspects of a 3D simulation, including lighting, position, size, texture, materials, and much more. The resulting pictures may also be further enhanced by using diffusion models with ControlNet.
Train and validate: In addition to pretrained computer vision models available on NVIDIA NGC, the NVIDIA DGX platform, a fully integrated hardware and software AI platform, may be utilized with physically based data to train or fine-tune AI models using frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or NVIDIA TAO. After training, reference apps such as NVIDIA Isaac Sim may be used to test the model and its software stack in simulation. Additionally, developers may use open-source frameworks like Isaac Lab to use reinforcement learning to improve the robot’s abilities.
In order to power a physical autonomous machine, such a humanoid robot or industrial automation system, the optimized stack may now be installed on the NVIDIA Jetson Orin and, eventually, the next-generation Jetson Thor robotics supercomputer.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#GenerativePhysicalAI#generativeAI#languagemodels#PyTorch#NVIDIAOmniverse#AImodel#artificialintelligence#NVIDIADGX#TensorFlow#AI#technology#technews#news#govindhtech
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
GIS In Our Daily Lives
The involvement of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in our daily lives is pervasive, influencing and enhancing various aspects across different sectors. The integration of GIS into everyday activities has become integral for decision-making, planning, and optimizing resources. GIS helps city planners and transportation experts to provide them with information like maps, satellite pictures, population statistics, and infrastructure data. GIS helps them make better decisions when designing cities and transportation systems that are sustainable and good for the environment.
The following points elucidate the notable involvement of GIS in our daily lives:
Navigation and Location Services: GIS provides monitoring functions through the visual display of spatial data and precise geographical positioning of monitored vehicles, whereas GPS provides accurate, clear, and precise information on the position and navigation of a monitored or tracked vehicle in real-time and at the exact location.GIS is at the core of navigation applications and location-based services on smartphones. It enables accurate mapping, real-time navigation, and geolocation services, assisting individuals in finding locations, planning routes, and navigating unfamiliar areas.
E-Commerce and Delivery Services: GIS software is a powerful tool for supply chain network planning. It helps determine the optimal location for distribution centers, warehouses, or other supply facilities. GIS is utilized in logistics and delivery services for optimizing routes, tracking shipments, and ensuring timely deliveries. E-commerce platforms leverage GIS to enhance the efficiency of their supply chain and last-mile delivery processes.
Weather Forecasting and Disaster Management: Many states are using GIS dashboard to monitor the rainfall across the state, on a real-time basis, from the data shared by rain sensors installed at various locationsGIS plays a crucial role in weather forecasting and disaster management. It assists meteorologists in analyzing spatial data, predicting weather patterns, and facilitating timely responses to natural disasters by mapping affected areas and coordinating emergency services.
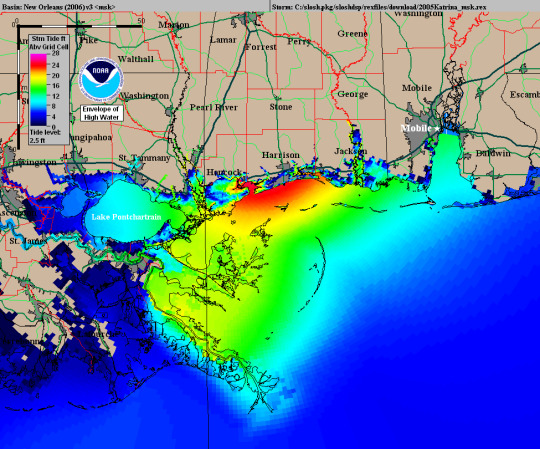
Healthcare Planning and Disease Monitoring: Geographic Information Systems enable the visualization and monitoring of infectious diseases. Additionally GIS records and displays the necessary information that health care needs of the community as well as the available resources and materials. GIS supports public health initiatives by mapping the spread of diseases, analyzing healthcare resource distribution, and assisting in the planning of vaccination campaigns. It aids in identifying high-risk areas and optimizing healthcare service delivery.
Social Media and Geo-tagging: GIS also helps in geotagging and other location related information in posts, it’s tools can map and visualize the spatial distribution of social media activity. This analysis can reveal trends, hotspots, and patterns in user engagement across different geographic areas. Many social media platforms incorporate GIS for geo-tagging, allowing users to share their location and experiences. This feature enhances social connectivity and facilitates the sharing of location-specific information.
Smart City Initiatives: The Geographic Information System (GIS) offers advanced and user-friendly capabilities for Smart City projects and allows to capture, store and manipulate, analyze and visualize spatially referenced data. It is used for spatial analysis and modeling. It is the cornerstone of smart city planning, enabling the integration of data for efficient urban management. It supports initiatives related to traffic management, waste disposal, energy consumption, and overall infrastructure development.
Education and Research: GIS is increasingly utilized in education and research for visualizing and analyzing spatial data. It enables students and researchers to explore geographic relationships, conduct field studies, and enhance their understanding of various subjects.

Agricultural Management and Precision Farming: Farmers leverage GIS to optimize agricultural practices by analyzing soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns. Precision farming techniques, facilitated by GIS, contribute to increased crop yields and sustainable farming practices.

Real Estate and Property Management: In the real estate sector, GIS aids in property mapping, land valuation, and site selection. It provides real estate professionals with valuable insights into spatial relationships, market trends, and optimal development opportunities.
Tourism and Recreation: GIS enhances the tourism industry by providing interactive maps, route planning, and location-based information. It assists tourists in exploring destinations, finding attractions, and navigating efficiently.
The broad and varied involvement of GIS in our daily lives underscores its significance as a technology that not only facilitates geographic data analysis but also contributes to the efficiency, safety, and interconnectedness of modern society. As GIS applications continue to evolve, their impact on daily activities is expected to further expand and refine.
#gis#architectdesign#architecture#city#education#geographic information system(gis)#geographical indication
14 notes
·
View notes